Updated:
As a maintainer of esp-idf-lib, I would like to test the library on ESP32S2, a single core version of ESP32. At the moment, the only ESP32S2 development board available from AliExpress — the only practically feasible distributor in the country where I live — is one from LilyGo. LilyGo, a Chinese manufacturer, has a broad range of ESP32 development boards. As their boards are kind of hit-or-miss, I chose the simplest development board for the test (TTGO T8 ESP32-S2-WOOR V1.1).

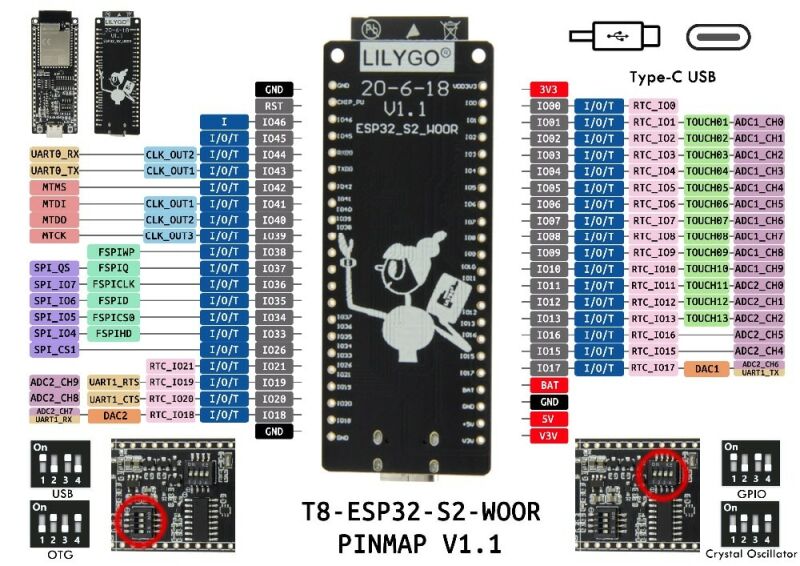
Product summary
| Chip | ESP32-S2-WROOM (datasheet) |
| SPI flash | 4MB (CONFIG_ESPTOOLPY_FLASHSIZE_4MB=y in `sdkconfig) |
| Has PSRAM | No |
| Has IPEX antenna | No (solder pad is available) |
| USB receptacle | Type C |
| USB serial | CH340C |
| Buttons | 2 (RESET, BOOT) |
| DIP switch | 2 |
| Number of pins | 44 (22 * 2) |
| LED | 1 (red) |
| Supports battery | Yes |
| Battery management IC | lithium-ion / lithium polymer rechargeable battery protection IC, S-8261 from ABLIC (the official datasheet and a copy at MOUSER) |
Pros
The PCB is narrow. Some ESP32 boards are a bit wide, which becomes an issue when using them on a breadboard. Two columns (one on each side) are available on a breadboard.
It comes with header pins, but they are not soldered.
It has no extra components, such as LCD or SD card slot, other than lithium rechargeable battery circuit (supports lithium ion and lithium polymer). Standby current of the whole circuit is unknown. It is a general purpose development board.
It has an ESP32-S2-WROOM module from ESPRESSIF, not original circuitry. Official modules are usually preferred — especially when you buy from Chinese manufacturers — because the core component is known to be good, the spec is documented by ESPRESSIF, and you have less uncertainty in the board.
A sample application (the GitHub repository) is burnt by default. You can test the board without any additional components. The sample scans available WiFi networks, prints the result, goes deep-sleep, and repeat. A nice application as an acceptance test.
Cons
The pinout is printed on the bottom layer. You cannot see pin numbers while developing.
Solder pads for header pins are small. You need to be bit careful when soldering. I used 0.8 mm solder wire, but 0.5 mm or less would be easier.
Silkscreen text is not big nor clear. Some texts are covered by pin headers, invisible after soldering.
Documentation is available (the product page), but sparse. For example, the two DIP switches are simply described as “USB/OTG” and “GPIO/Crystal Oscillator”. The schematic is not available.
The sample application
Here is the output from the original factory firmware.
ESP-ROM:esp32s2-rc4-20191025
Build:Oct 25 2019
rst:0x1 (POWERON),boot:0x8 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
SPIWP:0xee
mode:DIO, clock div:2
load:0x3ffe8100,len:0x4
load:0x3ffe8104,len:0x17d0
load:0x40050000,len:0x14b0
load:0x40054000,len:0x210c
SHA-256 comparison failed:
Calculated: e4c00e2375ff1fafbe29bcb3b7e27b9c9c95d933873037d414b5a12d7b6461ef
Expected: cc4e2de553ae5da28442dbb451bacba9c3f1a945b67d4ca835db7eb2b91950b4
Attempting to boot anyway...
entry 0x400502d8
I (66) boot: ESP-IDF v4.2-dev-1905-g625bd5eb18-dirty 2nd stage bootloader
I (66) boot: compile time 13:43:25
I (67) boot: chip revision: 0
I (70) boot.esp32s2: SPI Speed : 40MHz
I (75) boot.esp32s2: SPI Mode : DIO
I (80) boot.esp32s2: SPI Flash Size : 4MB
I (85) boot: Enabling RNG early entropy source...
I (90) boot: Partition Table:
I (94) boot: ## Label Usage Type ST Offset Length
I (101) boot: 0 nvs WiFi data 01 02 00009000 00006000
I (108) boot: 1 phy_init RF data 01 01 0000f000 00001000
I (116) boot: 2 factory factory app 00 00 00010000 00100000
I (124) boot: End of partition table
I (128) esp_image: segment 0: paddr=0x00010020 vaddr=0x3f000020 size=0x16acc ( 92876) map
I (163) esp_image: segment 1: paddr=0x00026af4 vaddr=0x3ffc84c0 size=0x03300 ( 13056) load
I (167) esp_image: segment 2: paddr=0x00029dfc vaddr=0x40024000 size=0x00404 ( 1028) load
I (170) esp_image: segment 3: paddr=0x0002a208 vaddr=0x40024404 size=0x05e10 ( 24080) load
I (186) esp_image: segment 4: paddr=0x00030020 vaddr=0x40080020 size=0x6bb3c (441148) map
I (310) esp_image: segment 5: paddr=0x0009bb64 vaddr=0x4002a214 size=0x0e2a4 ( 58020) load
I (329) esp_image: segment 6: paddr=0x000a9e10 vaddr=0x40070000 size=0x0001c ( 28) load
I (329) esp_image: segment 7: paddr=0x000a9e34 vaddr=0x50000000 size=0x00008 ( 8) load
I (347) boot: Loaded app from partition at offset 0x10000
I (347) boot: Disabling RNG early entropy source...
I (348) cache: Instruction cache : size 8KB, 4Ways, cache line size 32Byte
I (355) cpu_start: Pro cpu up.
I (359) cpu_start: Application information:
I (364) cpu_start: Project name: scan
I (368) cpu_start: App version: v4.2-dev-1905-g625bd5eb18-dirty
I (375) cpu_start: Compile time: Jun 22 2020 13:42:56
I (381) cpu_start: ELF file SHA256: fa3131b6ea9b57aa...
I (387) cpu_start: ESP-IDF: v4.2-dev-1905-g625bd5eb18-dirty
I (394) cpu_start: Single core mode
I (399) heap_init: Initializing. RAM available for dynamic allocation:
I (406) heap_init: At 3FFD0EF8 len 0002B108 (172 KiB): DRAM
I (412) heap_init: At 3FFFC000 len 00003A10 (14 KiB): DRAM
I (418) cpu_start: Pro cpu start user code
I (481) spi_flash: detected chip: generic
I (482) spi_flash: flash io: dio
I (482) cpu_start: Starting scheduler on PRO CPU.
I (486) scan: Not a deep sleep reset
I (486) scan: Turning on the peripherals power
I (3506) wifi:wifi driver task: 3ffd8bec, prio:23, stack:3584, core=0
I (3506) system_api: Base MAC address is not set
I (3506) system_api: read default base MAC address from EFUSE
I (3516) wifi:wifi firmware version: 0507408
I (3516) wifi:wifi certification version: v7.0
I (3516) wifi:config NVS flash: enabled
I (3516) wifi:config nano formating: disabled
I (3526) wifi:Init dynamic tx buffer num: 32
I (3526) wifi:Init data frame dynamic rx buffer num: 32
I (3536) wifi:Init management frame dynamic rx buffer num: 32
I (3536) wifi:Init management short buffer num: 32
I (3546) wifi:Init static rx buffer size: 1600
I (3546) wifi:Init static rx buffer num: 10
I (3556) wifi:Init dynamic rx buffer num: 32
I (3696) phy: phy_version: 303, c1e745d, Apr 11 2020, 14:22:04, 0, 2
I (3696) wifi:enable tsf
I (3696) wifi:mode : sta (7c:df:a1:01:fb:72)
I (5806) scan: Total APs scanned = 14
I (5806) scan: SSID makers
I (5806) scan: RSSI -45
I (5806) scan: Authmode WIFI_AUTH_WPA2_PSK
I (5806) scan: Pairwise Cipher WIFI_CIPHER_TYPE_CCMP
I (5816) scan: Group Cipher WIFI_CIPHER_TYPE_CCMP
I (5816) scan: Channel 9
...
Building application for ESP32S2
You need the latest master branch of esp-idf (pre-v4.2 as of this writing).
For general information about the development environment, see Get Started.
You need to install xtensa-esp32s2-elf toolchain. See xtensa-esp32s2-elf section in the official documentation. For FreeBSD users, I created a FreeBSD port.
To build applications for ESP32S2, you need to set the target (the default is ESP32).
idf.py set-target esp32s2
Make sure CONFIG_ESPTOOLPY_FLASHSIZE_4MB=y in sdkconfig. The sdkconfig in the repository has CONFIG_ESPTOOLPY_FLASHSIZE_2MB=y, which is not correct because ESP32-S2-WROOM has 4MB SPI flash (the menu is under Serial flasher config -> Flash size).
idf.py menuconfig
idf.py -p /path/to/serialport flash monitor
The following output is the same application built with the latest esp-idf (2020-11-18, 178b122c145c19e94ac896197a3a4a9d379cd618)
ESP-ROM:esp32s2-rc4-20191025
Build:Oct 25 2019
rst:0x1 (POWERON),boot:0x8 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
SPIWP:0xee
mode:DIO, clock div:2
load:0x3ffe6100,len:0x8
load:0x3ffe6108,len:0x1854
load:0x4004c000,len:0x9d8
load:0x40050000,len:0x2e34
entry 0x4004c1ec
I (49) boot: ESP-IDF v4.3-dev-1901-g178b122c1-dirty 2nd stage bootloader
I (49) boot: compile time 03:13:47
I (49) boot: chip revision: 0
I (52) boot.esp32s2: SPI Speed : 40MHz
I (57) boot.esp32s2: SPI Mode : DIO
I (62) boot.esp32s2: SPI Flash Size : 4MB
I (67) boot: Enabling RNG early entropy source...
I (72) boot: Partition Table:
I (76) boot: ## Label Usage Type ST Offset Length
I (83) boot: 0 nvs WiFi data 01 02 00009000 00006000
I (90) boot: 1 phy_init RF data 01 01 0000f000 00001000
I (98) boot: 2 factory factory app 00 00 00010000 00100000
I (105) boot: End of partition table
I (110) esp_image: segment 0: paddr=0x00010020 vaddr=0x3f000020 size=0x15dd0 ( 89552) map
I (144) esp_image: segment 1: paddr=0x00025df8 vaddr=0x3ffc86c0 size=0x039d8 ( 14808) load
I (148) esp_image: segment 2: paddr=0x000297d8 vaddr=0x40024000 size=0x00404 ( 1028) load
I (151) esp_image: segment 3: paddr=0x00029be4 vaddr=0x40024404 size=0x06434 ( 25652) load
I (168) esp_image: segment 4: paddr=0x00030020 vaddr=0x40080020 size=0x69a5c (432732) map
I (288) esp_image: segment 5: paddr=0x00099a84 vaddr=0x4002a838 size=0x0de7c ( 56956) load
I (308) esp_image: segment 6: paddr=0x000a7908 vaddr=0x40070000 size=0x0002c ( 44) load
I (308) esp_image: segment 7: paddr=0x000a793c vaddr=0x50000000 size=0x00008 ( 8) load
I (325) boot: Loaded app from partition at offset 0x10000
I (326) boot: Disabling RNG early entropy source...
I (337) cache: Instruction cache : size 8KB, 4Ways, cache line size 32Byte
I (337) cpu_start: Pro cpu up.
I (392) cpu_start: Pro cpu start user code
I (392) cpu_start: cpu freq: 160000000
I (392) cpu_start: Application information:
I (394) cpu_start: Project name: scan
I (399) cpu_start: App version: 69d65af-dirty
I (405) cpu_start: Compile time: Dec 4 2020 03:14:09
I (411) cpu_start: ELF file SHA256: 0e600ec1a30a9b24...
I (417) cpu_start: ESP-IDF: v4.3-dev-1901-g178b122c1-dirty
I (424) heap_init: Initializing. RAM available for dynamic allocation:
I (431) heap_init: At 3FF9E02C len 00001FD4 (7 KiB): RTCRAM
I (437) heap_init: At 3FFCFD88 len 0002C278 (176 KiB): DRAM
I (443) heap_init: At 3FFFC000 len 00003A10 (14 KiB): DRAM
I (450) spi_flash: detected chip: generic
I (454) spi_flash: flash io: dio
I (462) cpu_start: Starting scheduler on PRO CPU.
I (464) scan: Not a deep sleep reset
I (464) scan: Turning on the peripherals power
I (3484) wifi:wifi driver task: 3ffd5f38, prio:23, stack:3584, core=0
I (3484) system_api: Base MAC address is not set
I (3484) system_api: read default base MAC address from EFUSE
I (3494) wifi:wifi firmware version: b9e8721
I (3494) wifi:wifi certification version: v7.0
I (3494) wifi:config NVS flash: enabled
I (3494) wifi:config nano formating: disabled
I (3504) wifi:Init data frame dynamic rx buffer num: 32
I (3504) wifi:Init management frame dynamic rx buffer num: 32
I (3514) wifi:Init management short buffer num: 32
I (3514) wifi:Init dynamic tx buffer num: 32
I (3524) wifi:Init static rx buffer size: 1600
I (3524) wifi:Init static rx buffer num: 10
I (3534) wifi:Init dynamic rx buffer num: 32
I (3534) wifi_init: rx ba win: 6
I (3534) wifi_init: tcpip mbox: 32
I (3544) wifi_init: udp mbox: 6
I (3544) wifi_init: tcp mbox: 6
I (3554) wifi_init: tcp tx win: 5744
I (3554) wifi_init: tcp rx win: 5744
I (3554) wifi_init: tcp mss: 1440
I (3564) wifi_init: WiFi IRAM OP enabled
I (3564) wifi_init: WiFi RX IRAM OP enabled
I (3694) phy: phy_version: 603, 72dfd77, Jul 7 2020, 19:57:05, 0, 2
I (3694) wifi:mode : sta (7c:df:a1:01:fb:72)
I (3694) wifi:enable tsf
I (5794) scan: Total APs scanned = 15
I (5806) scan: SSID makers
I (5806) scan: RSSI -45
I (5806) scan: Authmode WIFI_AUTH_WPA2_PSK
I (5806) scan: Pairwise Cipher WIFI_CIPHER_TYPE_CCMP
I (5816) scan: Group Cipher WIFI_CIPHER_TYPE_CCMP
I (5816) scan: Channel 9
...
To buy or not to buy
I am generally happy with the board. It is a simple, breadboard-friendly development board. However, the silkscreen issue is a major drawback. When WROOM or WROVER module is used, there is little space left for pin numbers. But it can be possible without sacrificing a column of breadboard (Lolin D32 Pro is an example). A good start but there will be better versions from LilyGo and other manufacturers. If you want to give ESP32S2 a try, then buy one or two. It costs just USD 5 excluding shipping fee (as of 2020-12-04).
